Module 10: Global Accelerator Assignment
Tasks To Be Performed:
- Create a Global Accelerator: a. Make an EC2 instance as an endpoint b. Make a load balancer as an endpoint and should be in a different region than the EC2 instance
I create an EC2 instance in the “us-east-1” region. This instance will host my test page, similar to ”Assignment 1 – EC2.”
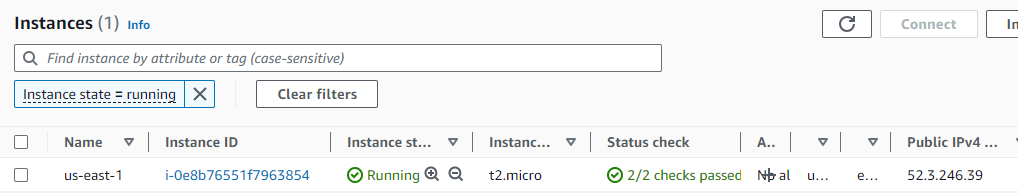
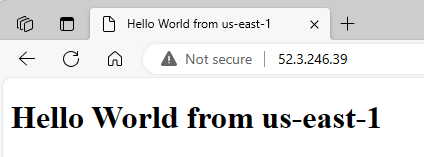
To ensure the page is successfully hosted, I access it using the provided public IPv4 address.
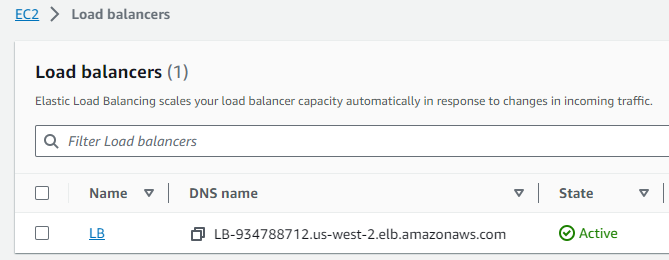
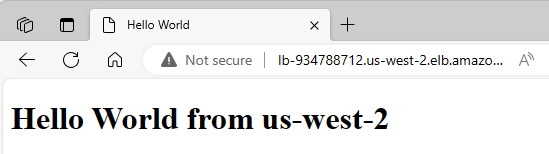
I set up a Load Balancer in the “us-west-2” region that directs traffic to my EC2 instance hosting the test page.
To verify the setup, I access the test page through the Load Balancer’s link. Successfully, the message “Hello World from us-west-2” appears, indicating the page is correctly routed through the Load Balancer.
I head to the AWS dashboard and click on the “Create accelerator” button. I then name the accelerator “myAccelerator”.
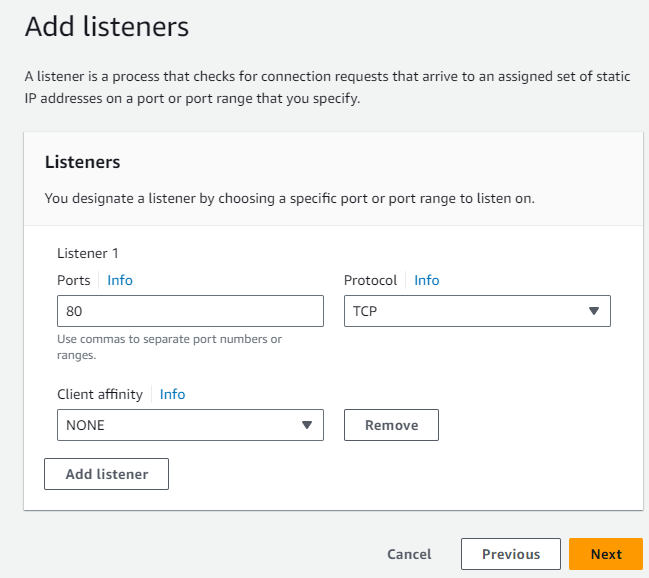
Next, I move on to configure the listeners. I set up a listener for port 80 using the TCP protocol, no client affinity set.
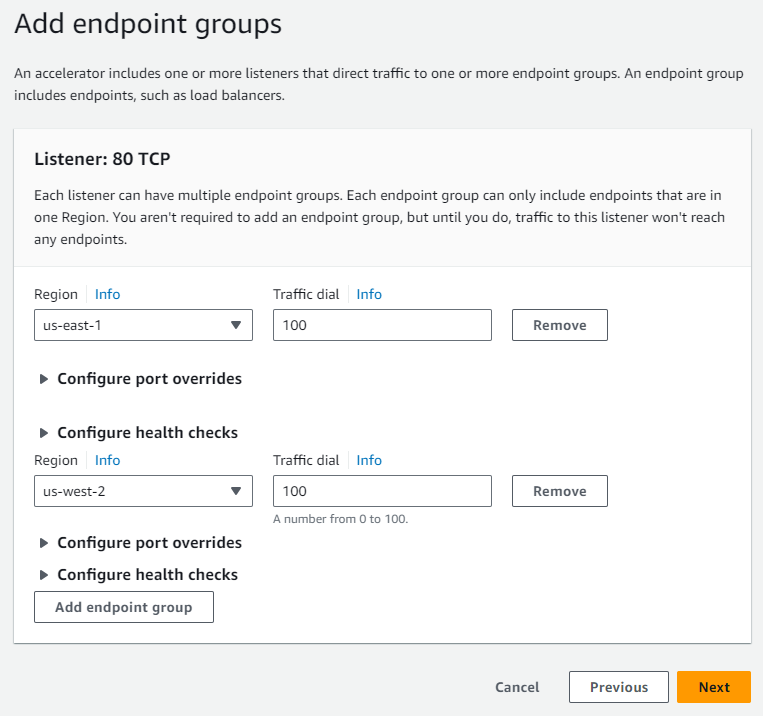
After setting up the listener, I proceed to add endpoint groups for both the “us-east-1” and “us-west-2” regions.
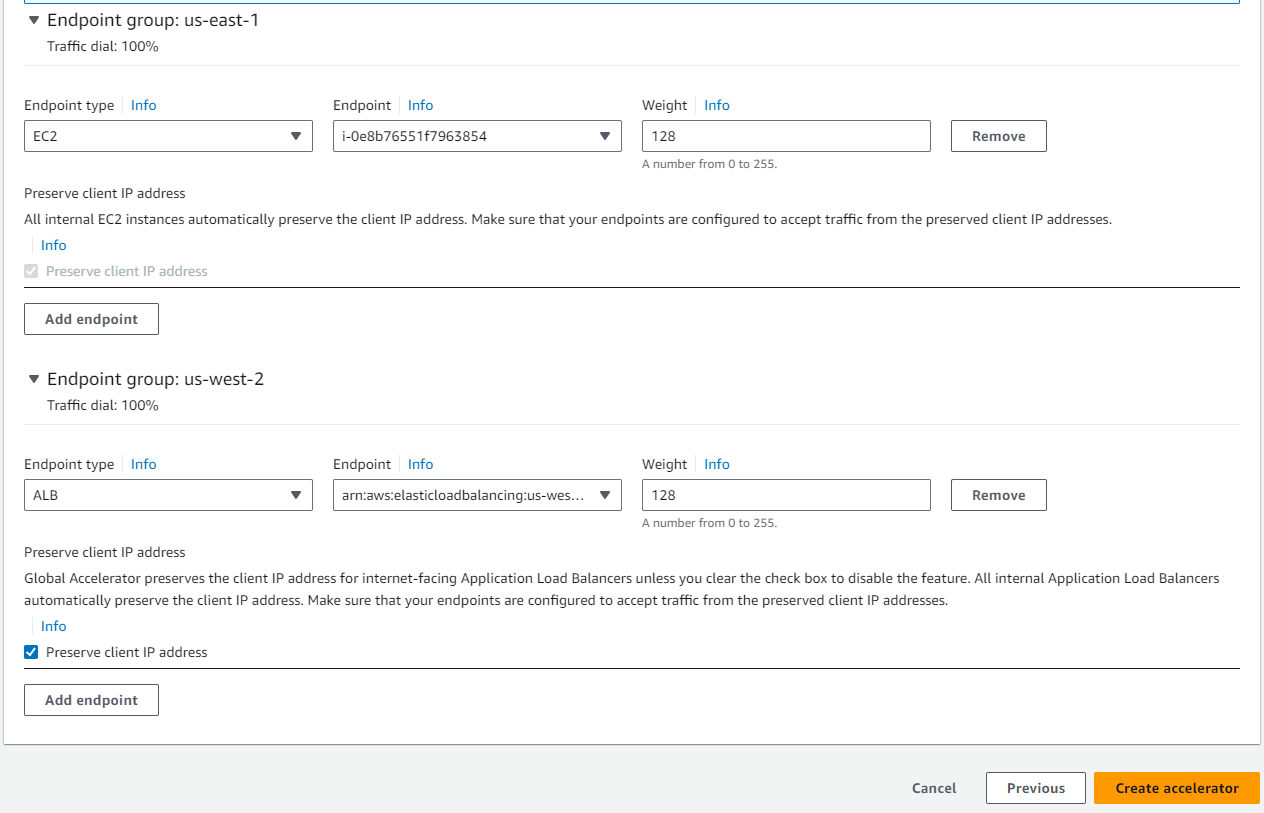
I add an endpoint for each endpoint group: the EC2 in “us-east-1” and the Load Balancer in “us-west-2”. Then, I click the “Create accelerator” button.
 The newly created Accelerator
The newly created Accelerator
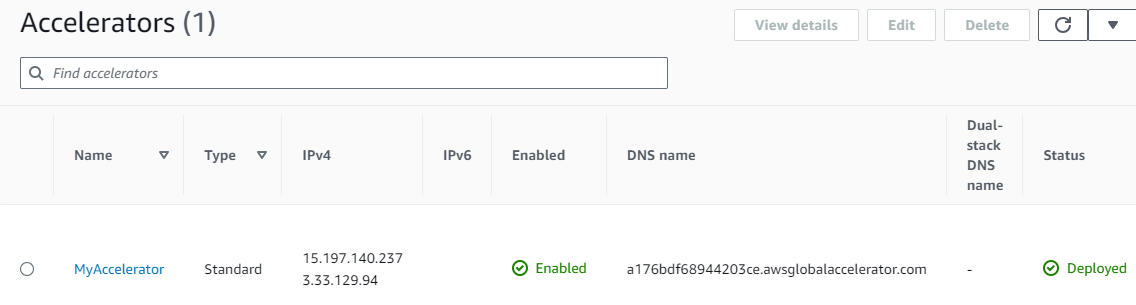
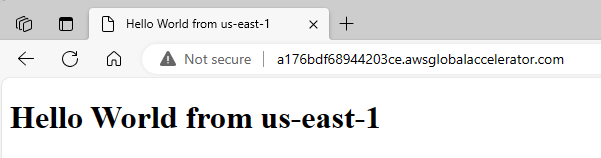
Now, I test the link of the accelerator, and it connects me to the EC2 in us-east-1. AWS Global Accelerator directs traffic to the optimal AWS endpoint based on health, geographic proximity, and routing policies configured. Being in Florida, I’m geographically closer to the US East 1 (Northern Virginia) AWS region than to US West 2 (Oregon).