Module 11: Migration Assignment - 3
Problem Statement: You work for XYZ Corporation. Your corporation wants to move their infrastructure to the cloud to improve the performance and availability of the application hosted. You are given the opportunity to accomplish the tasks for successful migration.
Tasks To Be Performed:
- Launch an RDS MySQL database. Login and insert some data into it.
- Use Database Migration (DMS) System to migrate the MySQL database into an RDS PostgreSQL database.
MySQL Database Setup and Data Generation
We set up an RDS instance with the MySQL Engine and an Aurora Cluster for Postgres. MySQL serves as our source database, while Postgres acts as our target.
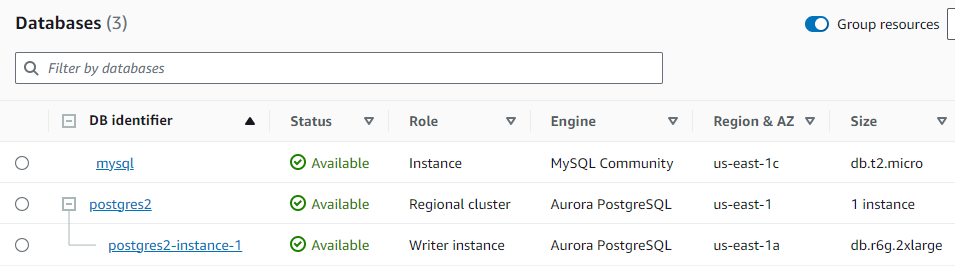
I will connect to these databases using an EC2 instance by selecting the “Set up EC2 connection” option for each database.
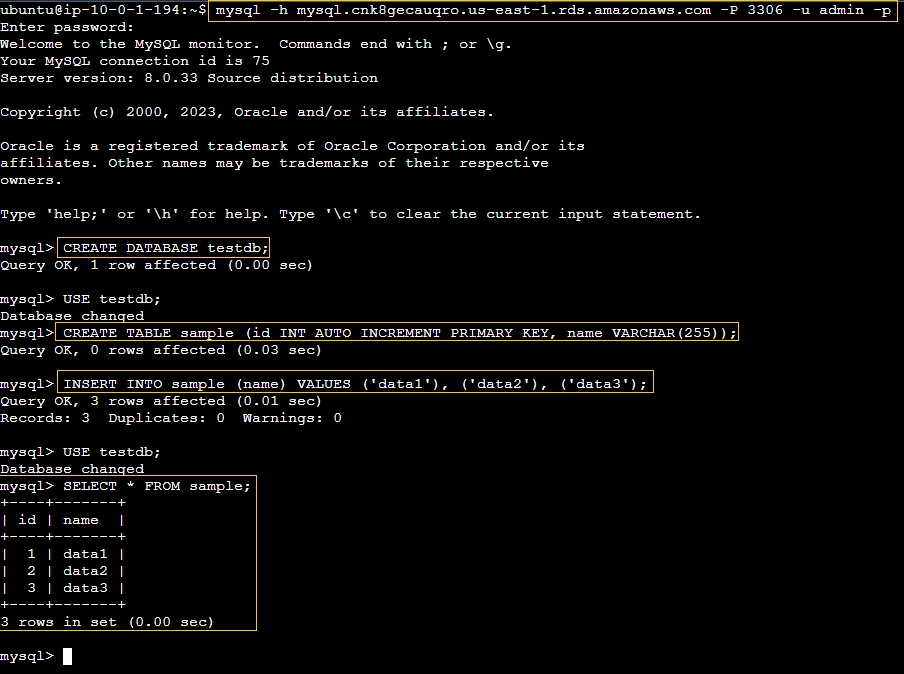
Connecting to the MySQL Instance
The provided MySQL script will generate a database and some sample data to migrate.
CREATE DATABASE testdb;
USE testdb;
CREATE TABLE sample (id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, name VARCHAR(255));
INSERT INTO sample (name) VALUES ('data1'), ('data2'), ('data3');Connecting to the MySQL instance hosted on Amazon RDS.
mysql -h mysql.cnk8gecauqro.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com -P 3306 -u admin -p
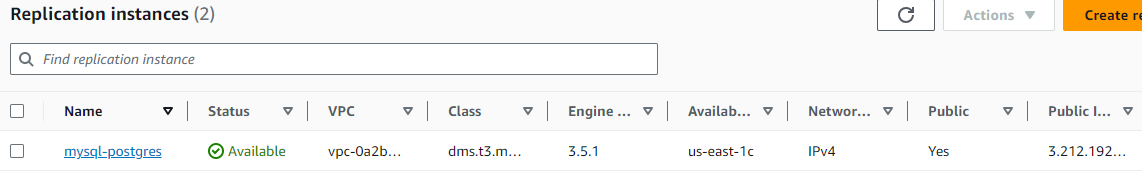
Creating a Replication Instance
To begin the data migration process using the AWS Database Migration Service (DMS), I first need to create a Replication Instance. Here’s the step-by-step procedure:
- Start by searching for “DMS” in the AWS Management Console.
- Once inside DMS, I navigate to the
Migrate datasection. - Then, I choose
Replication instances. - On this screen, I’ll click on the button titled “Create replication instance”.
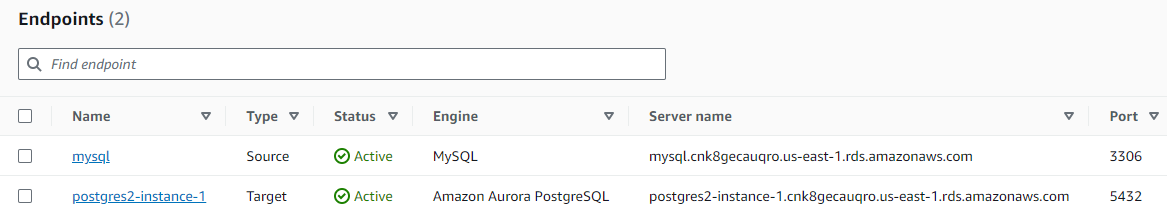
Setting Up Source and Target Endpoints
To set up the endpoints for our migration process, here’s what I do:
For the MySQL Source Endpoint:
- In the AWS DMS console, I navigate to the left panel and click on
Migrate data. - Next, I select
Endpoints. - I then click on the “Create endpoint” button.
- In the setup, I ensure I select MySQL as the source type and provide the necessary database details.
For the PostgreSQL Target Endpoint:
- Still within the
Endpointssection, I click on another “Create endpoint” button. - This time, I set it up for our PostgreSQL database, specifying it as our target.
- I provide the required Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL details and finish the configuration.
Database Migration Task
To initiate the actual data migration process, here’s what I’m doing:
- In the AWS DMS console, I head over to the left panel and select
Migrate data. - I then choose
Database migration tasks. - To kick off the migration, I click on the “Create task” button.
- I pick the previously created replication instance
- I ensure that the correct source (MySQL) and target (PostgreSQL) endpoints are selected.
- With the task configured, I begin the migration. As seen in the dashboard, the task with the identifier
mysql-postgreshas successfully completed a full load, transferring 100% of the data from the MySQL source to the PostgreSQL target. This confirms our data has been moved successfully.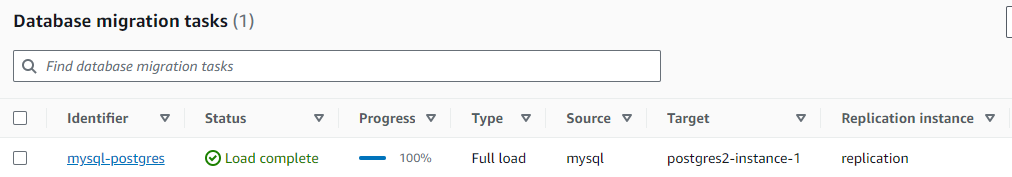
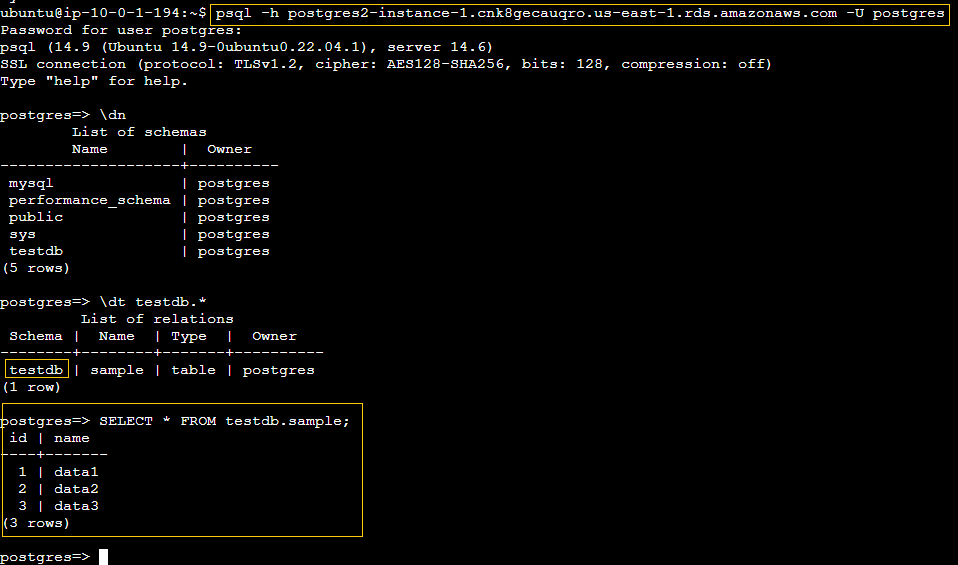
Verifying Data Migration in PostgreSQL
To verify the data migration, I’m connecting to the PostgreSQL instance using the provided command. This will allow me to access the PostgreSQL database and inspect the tables and data to ensure everything was migrated accurately from the MySQL source.
psql -h postgres2-instance-1.cnk8gecauqro.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com -U postgres
Success